Instructions for Clinical Staff
The Academy’s data indicate that aid-in-dying medications can be administered effectively through a small rectal catheter, PEG or other feeding tube, or through ostomies, provided patients undergo proper medical screening, are well-prepared, and receive adequate support. Non-oral administration requires specialized clinical expertise, close coordination between the prescribing clinician and bedside team, and the presence of trained medical personnel on the day of aid-in-dying. We encourage prescribers to collaborate with bedside clincal staff, espeically hospice nurses!
The Academy strongly recommends that all patients considering aid in dying enroll in hospice care—especially those who might need help with non-oral self-administration. Since terminal conditions can change rapidly, thorough palliative support and realistic contingency planning are essential. Some hospices fully train and equip their staff to support patients considering aid in dying, including those who may need non-oral routes.
We encourage prescribers to collaborate with bedside clincal staff, espeically hospice nurses!
For referrals to hospices or other providers experienced in non-oral routes, please complete our intake form at this link.
Note: Recommendations for ostomy administration are currently under review.
For immediate assistance, contact our clinical advisors:
Thalia DeWolf, RN, CHPN : thalia@aadm.org Or contact our hotline: AADM Clinicians’ Hotline
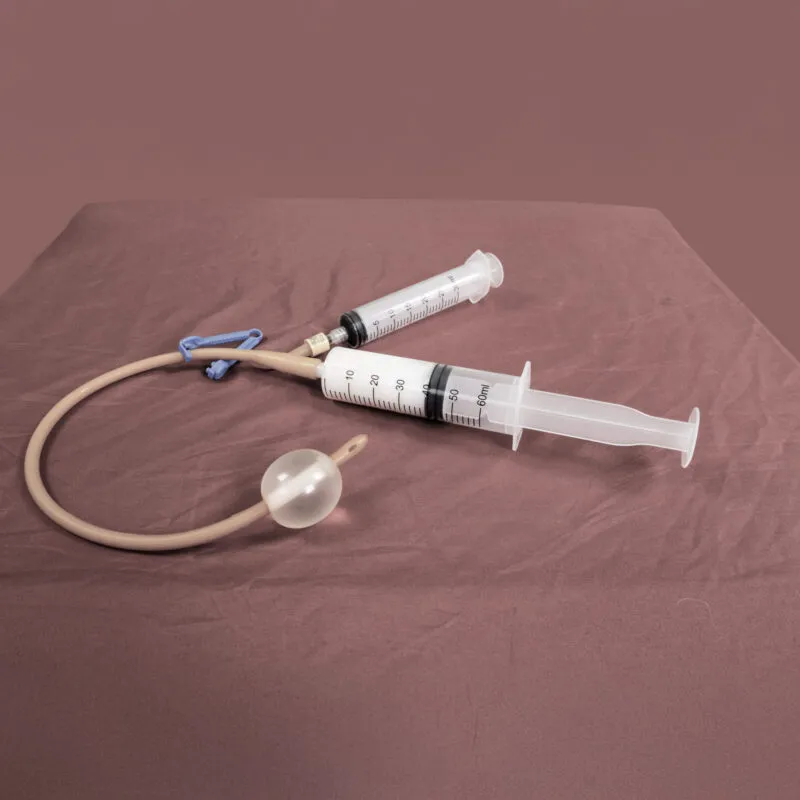
Clinician Instructions for Rectal Administration of Aid in Dying
Click here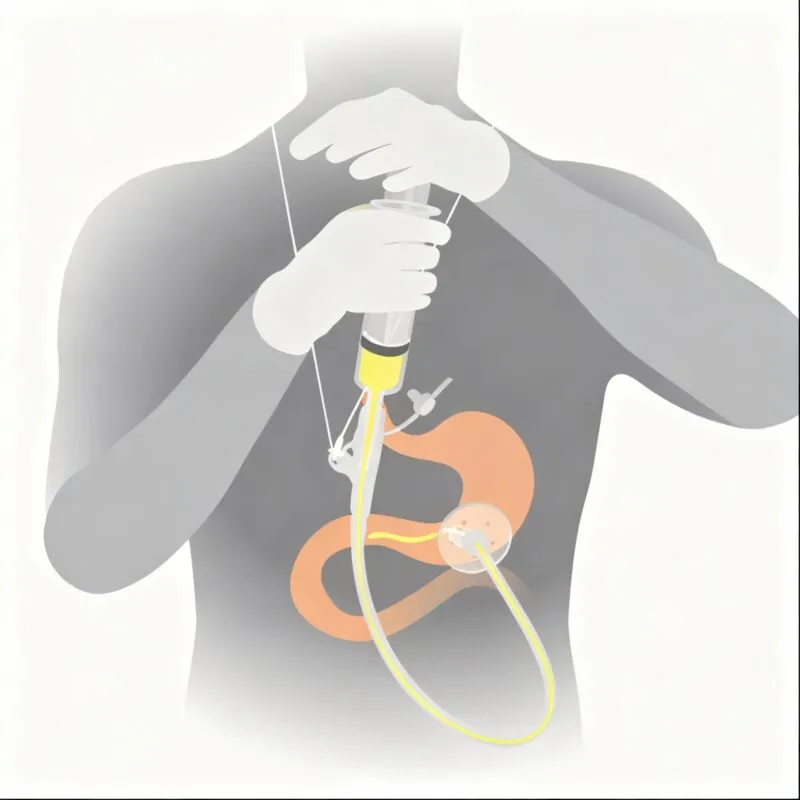
Clinician Instructions for PEG Administration of Aid in Dying
Click hereOstomy administration recommendations are currently under review. For immediate assistance, contact: Thalia DeWolf, RN, CHPN – thalia@aadm.org Or contact the Academy Clinicians Hotline: AADM Clinicians’ Hotline